Understanding Solar Power Generation
Solar power has emerged as one of the most promising renewable energy sources in the world today. By converting sunlight directly into electricity, solar power is not just a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels but also a sustainable one. In this blog, we will explore how solar power is generated, breaking down the process into easily understandable steps.
1. What is Solar Power?

Solar power is energy derived from sunlight. It is harnessed using various technologies, with solar panels being the most common method. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used in homes, businesses, and for powering devices.
2. The Key Components of Solar Power Generation
Before we dive into the solar power generation process, let’s familiarize ourselves with its key components:
- Solar Panels (Photovoltaic Cells): These are the heart of the solar power system. They are made of silicon and other materials that create an electric field when exposed to sunlight.
- Inverter: This device converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used in most homes and businesses.
- Mounting Systems: These support the solar panels, ensuring they are positioned to capture maximum sunlight.
- Battery Storage (optional): Some systems include batteries that store excess energy produced during the day for use at night or during cloudy weather.
3. How Solar Power is Generated
Step 1: Sunlight Absorption

When sunlight hits a solar panel, it energizes the electrons in the silicon cells, causing them to move. This movement generates a flow of electricity.
Step 2: Generation of Direct Current (DC)
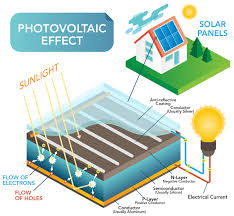
The flow of electrons within the solar cells produces direct current (DC) electricity. This is the initial form of electricity that the solar panels generate.
Step 3: Conversion to Alternating Current (AC)

Since most appliances and electrical devices use alternating current (AC), the DC electricity produced must be converted using an inverter. The inverter converts the DC electricity into AC electricity for home use.
Step 4: Powering Your Facility

Once the electricity has been converted to AC, it is sent to the electrical panel of your facility, where it can be used to power lights, appliances, and other electrical devices.
Step 5: Net Metering and Battery Storage
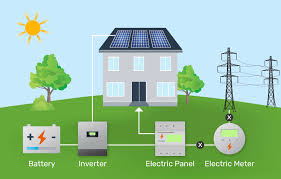
If your solar power system generates more energy than you use, you can send the excess back to the grid through a net metering system. Additionally, if your system is equipped with battery storage, you can store excess electricity for later use during low sunlight hours.
4. Environmental Benefits of Solar Power
Solar power not only helps reduce electricity bills but also plays a significant role in reducing carbon footprints. It’s a clean, renewable source of energy that helps combat climate change.
Conclusion
Solar power generation is a simple yet effective way to harness the energy of the sun. As technology continues to improve, solar energy will become more efficient and accessible, paving the way for a sustainable future. Whether you’re looking to reduce your energy bills or make a positive environmental impact, understanding how solar power is generated is the first step towards embracing this clean energy source.
